Understanding the Link Between Diabetes and Heart Health
Diabetes and heart health are deeply intertwined. As a cardiologist, I frequently see patients with diabetes who also face heart-related issues. Here’s a closer look at how these two conditions are connected and why managing your diabetes is crucial for protecting your heart.
How Diabetes Impacts the Heart
When you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels can spike and remain high for extended periods. Over time, these elevated levels damage the blood vessels and nerves responsible for regulating your heart. This increases your risk for heart diseases like coronary artery disease, heart failure, and even strokes.
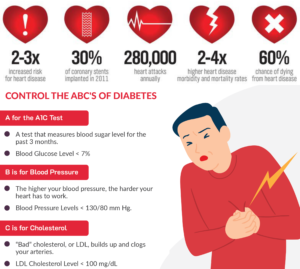
Studies have shown that people with diabetes are up to five times more likely to develop heart failure than those without diabetes. This risk isn’t just limited to one form of heart disease—both systolic (pumping dysfunction) and diastolic (filling dysfunction) heart failure are more common in diabetics.
High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Key Players in Heart Risk
Diabetes often leads to other cardiovascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol. These conditions strain your heart and accelerate the damage done to blood vessels.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is particularly dangerous for diabetics. It forces the heart to work harder to pump blood, and over time, this increased workload can damage both the heart and blood vessels. Adding to the mix, cholesterol can build up in the arteries, forming plaques that reduce blood flow, increasing the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
Research from the World Health Organization highlights that more than 60% of diabetics will die from heart disease or stroke, making it critical to keep blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check.
Obesity and Inflammation: The Hidden Heart Threats
For those with Type 2 diabetes, being overweight is often a significant contributing factor. Excess weight not only makes it harder to manage blood sugar but also increases the likelihood of developing high blood pressure and high cholesterol—both of which strain the heart.
Additionally, diabetes is associated with chronic inflammation, which silently damages blood vessels and increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. This inflammation, coupled with poor blood sugar control, weakens the heart’s function over time.
The Diabetes and Heart Disease Cycle
Heart disease and diabetes create a dangerous cycle. Diabetes can lead to heart disease, but having heart disease can also make it harder to control diabetes. Poor heart function complicates blood flow, affecting the body’s ability to regulate glucose levels. This vicious cycle can accelerate complications, making it crucial for diabetics to focus on both heart health and blood sugar management.
A study by the National Institute of Health found that individuals with diabetes and heart disease face more severe complications and worse outcomes than those without diabetes, highlighting the importance of proactive management.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Heart with Diabetes
Though diabetes poses a significant risk to heart health, there are steps you can take to reduce that risk. Managing your blood sugar, maintaining a healthy weight, and addressing other risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol are key to preventing heart complications.
Living a heart-healthy lifestyle—by exercising, eating a balanced diet, and taking your medications—can make all the difference in managing both diabetes and heart disease. By taking these steps, you can break the cycle and protect your heart for the long term.
Stay tuned for more tips on how to manage diabetes and heart health effectively!
Click here for previous blog